Vitamin E: what is tocopherol used for?
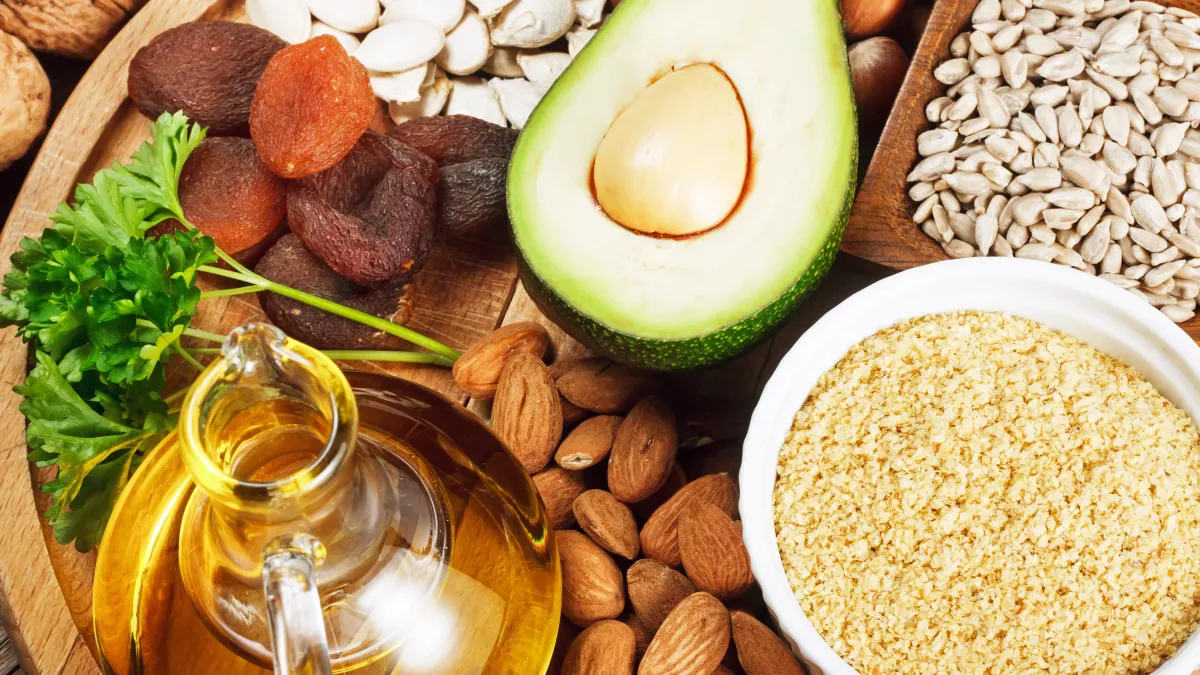
Vitamin E, also called tocopherol, is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for the proper functioning of the body. Antioxidant, it also helps protect the cardiovascular and nervous systems and promote fertility. It is mainly found in vegetable oils.
Characteristics of vitamin E:
- Fat-soluble vitamin in the same way as vitamins A, D and K
- Helps fight oxidative stress and cellular aging
- Vegetable oils and oilseeds are rich in it
- Acts synergistically with vitamin C, selenium and zinc
- Formerly known as the X factor
Why consume foods rich in vitamin E?
Vitamin E: benefits and roles in the body
Anti-oxidant function
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant, it acts in synergy with other molecules such as vitamin C, selenium and zinc. A good intake of vitamin E thus helps neutralize excess free radicals and fight against oxidative stress and premature cellular aging. Antioxidants also protect the body from various pathological processes: inflammation, cancers, etc.
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Tocopherol constitutes and preserves membrane lipids. It has a protective effect on the cardiovascular system. In addition, its anti-inflammatory effect limits the process of atherosclerosis, a risk factor for cardiovascular accidents. Sufficient consumption of vitamin E could, therefore, reduce mortality from cardiovascular accidents.
Protection against AMD and neurodegenerative diseases
By fighting against oxidative stress, vitamin E could have promising effects on cognitive functions and visual acuity. As such, studies are still underway but seem to highlight the positive effect of this vitamin on various conditions such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cataracts, Alzheimer’s disease, etc.
Vitamin E and skin
A good intake of vitamin E helps maintain healthy skin. This fat-soluble vitamin enters into the constitution of cell membranes and gives elasticity and plasticity to the skin. In addition, its anti-oxidant action helps fight against skin aging.
Foods rich in vitamin E
Vitamin E is mainly found in vegetable oils and oilseeds. To ensure a good daily intake of vitamin E, it is strongly recommended to vary vegetable oils and consume them with each meal.
|
Food |
Portions |
(mg) |
|
Wheat germ oil |
15 ml (1.5 tbsp) |
21 mg |
|
Unblanched almonds, roasted dry or in oil, or dehydrated |
60ml (1/4 cup) |
9-18 mg |
|
Dry Roasted Sunflower Seeds |
60ml (1/4 cup) |
8 mg |
|
Hazelnuts, unblanched filberts, dry roasted |
60ml (1/4 cup) |
5-8 mg |
|
Sunflower oil |
15 ml (1.5 tbsp) |
6 mg |
|
Safflower oil |
15 ml (1.5 tbsp) |
5 mg |
|
Breakfast cereals, 100% bran (All Bran type) |
30 g |
3-5 mg |
|
Pine nuts |
60ml (1/4 cup) |
3 mg |
|
Roasted peanuts in oil |
60ml (1/4 cup) |
2-3 mg |
|
Canned tomato paste |
60ml (1/4 cup) |
3 mg |
|
Canned tomato puree |
125ml (1/2 cup) |
3 mg |
|
Dried Brazil nuts |
60ml (1/4 cup) |
2 mg |
|
Mixed nuts, roasted in oil or dry |
60ml (1/4 cup) |
2 mg |
|
Fish eggs, various species |
30 ml (3 tbsp) |
2 mg |
|
Corn or wheat bran, raw |
30 g |
2 mg |
|
Peanut, olive, rapeseed or corn oil |
15 ml (1.5 tbsp) |
2 mg |
|
Lawyer |
½ avocat (100 g) |
2 mg |
|
Canned sardines, with bones |
100 g |
2 mg |
|
Asparagus, boiled or raw |
125ml (1/2 cup) |
1-2 mg |
|
Boiled spinach |
125ml (1/2 cup) |
1-2 mg |
Use of vitamin E
Vitamin E requirements
|
Recommended nutritional intake (ANC) |
|
|
Babies 0-6 months |
4 mg* |
|
Babies 7-12 months |
5 mg* |
|
Babies 1-3 years old |
6 mg |
|
Children 4-8 years old |
7 mg |
|
Boys 9-13 years old |
11 mg |
|
Girls 9-13 years old |
11 mg |
|
Boys 14-18 years old |
15,5 mg |
|
Girls 14-18 years old |
10 mg |
|
Men 19-75 years old |
15,5 mg |
|
Women 19-75 years old |
10 mg |
|
Men aged 75 and over |
20 to 50 mg |
|
Women aged 75 and over |
20 to 50 mg |
|
Pregnant women |
12 mg |
|
Breastfeeding women |
12 mg |
* Sufficient intakes
Tocopherol-based food supplements
Food supplements based on vitamin E are often indicated for their antioxidant power which helps fight oxidative stress and promotes optimal health. The dosage varies depending on the problem and the context. As excess vitamin E is not without consequences, it is recommended to seek medical advice.
Adverse effects of tocopherol
Consequences of vitamin E deficiency
Although extremely rare in France, vitamin E deficiency can affect the nervous system and muscles and cause coordination problems. It can also be the cause of hemolytic anemia in young children.
Consequences of excess vitamin E
Since vitamin E is fat-soluble, the body can store it in adipose tissue. Therefore, an overdose is entirely possible. The main risk linked to excess vitamin E in the long term is hemorrhagic. The competent authorities recommend not exceeding a consumption of 62 mg of vitamin E per day in adults.
 Receive every day
Receive every day
advice from our experts
to take care of you

Interactions with other nutrients
In the body, vitamin E acts in synergy with vitamin C, selenium and zinc to provide an optimal antioxidant effect.
The greater the consumption of unsaturated fatty acids (Omega 3, 6 and 9), the greater the intake of vitamin E must be in order to protect them from oxidation within the body.
Chemical properties
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin composed of eight molecules, four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. It acts in synergy with other antioxidant molecules and helps neutralize free radicals in the body. In the food industry, vitamin E is also used as a food additive (E306) for its anti-oxidant properties.
Historical
Nutrient History
Vitamin E was discovered in 1922 by two researchers in California. By putting a group of female mice on a low-fat diet, they discovered that they could become pregnant but the fetuses were unable to develop. Vitamin E was first named factor X and recognized as essential for fetal development.
In 1924, another study demonstrated the essential nature of vitamin E on animal fertility. It will then be named tocopherol from the Greek “bear and offspring”. Despite all these advances, it was not until 1968 that tocopherol was recognized as essential for human health.

Nutrition Center
January 2012

Dietitian Nutritionist
June 2018
96% Readers found this article helpful And you ?
Was this article useful to you?